ttps://lymphsystemsupport.com/presentation
ttps://lymphsystemsupport.com/presentation

Dr. Ann Shippy
Board Certified Internal Medicine and Functional Medicine Physician. Austin, Texas.
All About the Lymphatic System
What’s the one system in the body connected to everything else and essential for cardiovascular health, immunity, and detoxification?
Hint: We don’t talk about it much, and we need to talk about it more.
It’s the lymphatic system!
Maybe you’ve heard about lymphatic massage or jumping on a trampoline to move lymph.
Still, most of the time, we don’t dive into lymph in medical conversations, even though dysfunction in the lymphatic system contributes to a host of symptoms and chronic disease.
And promoting lymph flow and restoring lymphatic health may be key pieces to healing.
Today’s article will cover the lymph system in detail.
You’ll learn more about the answers to these questions:
- What is the lymphatic system?
- What’s the difference between lymph, lymph nodes, and lymphatic drainage?
- What does the lymphatic system do?
- What goes wrong with the lymphatic system?
- How can you improve and support the lymphatic system?
What Is the Lymphatic System?
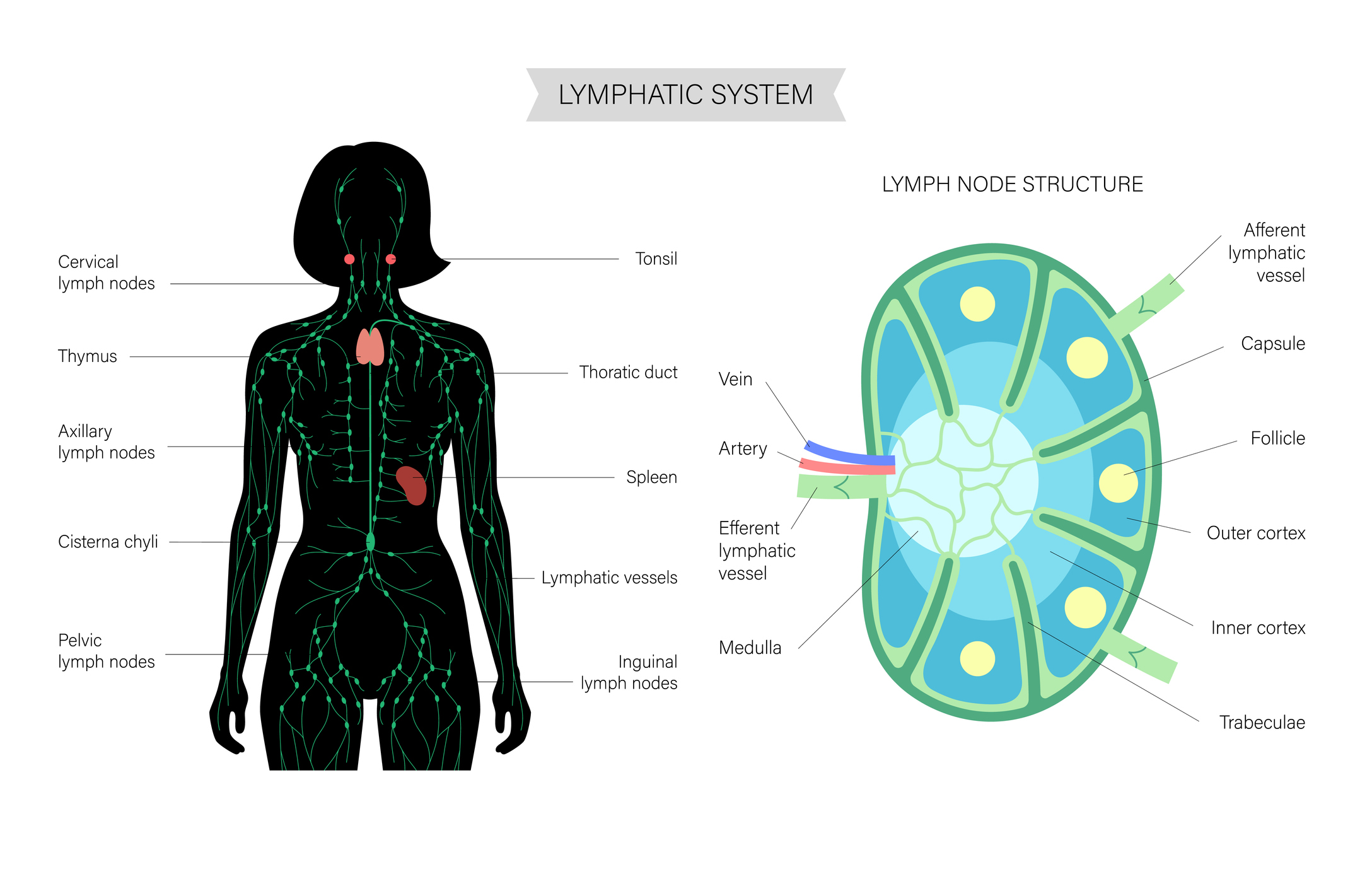
The lymphatic system, or lymphatic drainage system, is a network of vessels, nodes, and organs that move a water-based fluid called lymph.
The flow of lymph through the lymphatic system is analogous to blood flow through veins.
However, unlike the cardiovascular system, where the heart pumps blood, lymph moves based on a pressure gradient and by body movements and muscle contractions.
The lymphatic system is composed of:
- Lymph vessels – tubes that transport lymph
- Lymph – the colorless, watery liquid that transports nutrients and waste from cells back to the bloodstream
- Lymph nodes – lymphatic tissue that houses immune cells and filters lymph. There are around 600 lymph nodes in the body.
- Lymphatic organs – organs containing lymphatic tissue include the spleen, thymus, tonsils, Peyer’s patches in the small intestine, and the appendix
- Lymphocyte – a type of white blood cell that includes B cells and T cells and is part of the immune system. Lymphocytes are concentrated in the lymphatic system and found in the blood and other tissues.
- Lymphatic muscles – composed of muscle cells specific to the lymph system that contract to move lymph
You’ll find the lymphatic system throughout the body, including the brain, where it plays a critical role in how the body functions.
 What Does the Lymphatic System Do?
What Does the Lymphatic System Do?
A primary role of the lymphatic system is to remove toxins and waste from cells.
It’s a critical part of the body’s clean-up crew!
Because the lymph system connects to all other systems in the body, it plays many essential roles, including:
- Maintains fluid balance and homeostasis
- Protects the body from pathogens
- Transports fats and fat-soluble vitamins from the digestive system into circulation
- Restores protein and fluid fro
- Maintains fluid balance and homeostasis
- Protects the body from pathogens
- Transports fats and fat-soluble vitamins from the digestive system into circulation
- Restores protein and fluid from spaces between cells back into circulation
- Detoxification
A relatively new discovery about the lymphatic system is that it exists in the brain and nervous system – called the glymphatic system, where it clears waste and may be necessary for preventing dementia.
